How to Understand U.S. Actions on Venezuelan Oil Funds

The relationship between the United States and Venezuela has been marked by deep economic, political, and social conflicts, primarily driven by U.S. sanctions and Venezuela’s vast oil reserves. In recent years, the U.S. government has taken a range of actions to manage Venezuelan oil assets and prevent further financial mismanagement. These measures are often tied to the country’s attempts to regain financial stability, but the U.S. has its own strategic interests. Understanding these actions can shed light on the broader geopolitical dynamics at play.
The U.S. Sanctions on Venezuela: A Complex History
Venezuela’s economic crisis, exacerbated by its dependency on oil revenues, led the U.S. to impose a series of sanctions aimed at curbing the country’s oil production and revenue generation. The sanctions target key figures within the Venezuelan government, the state-owned oil company PDVSA, and other key sectors.
Key Sanctions:
Asset Freezes: The U.S. froze the assets of Venezuelan officials and entities involved in the country’s oil production and export.
Restrictions on Oil Exports: The U.S. prohibited American companies from purchasing Venezuelan crude oil, severely impacting the country’s oil-dependent economy.
Blocking Access to U.S. Financial System: Venezuela’s ability to access international markets was further restricted, creating difficulties in handling debts and acquiring resources.
How Much Does Venezuela Owe U.S. Oil Companies?
Venezuela’s debt to U.S. oil companies is one of the major issues complicating the country’s oil exports. Over the years, Venezuelan oil companies have accumulated billions in unpaid debts to American firms. Despite its massive oil reserves, Venezuela’s economic instability, partly caused by the U.S. sanctions, has made it difficult for the country to fulfill these obligations.
Why Does Venezuela Owe the U.S. Oil?
Venezuela’s state-run oil company, PDVSA, has struggled with production declines and mismanagement. The U.S. oil companies that once had joint ventures with PDVSA are among those left waiting for payment. These debts have piled up, leaving Venezuela vulnerable to further economic sanctions.
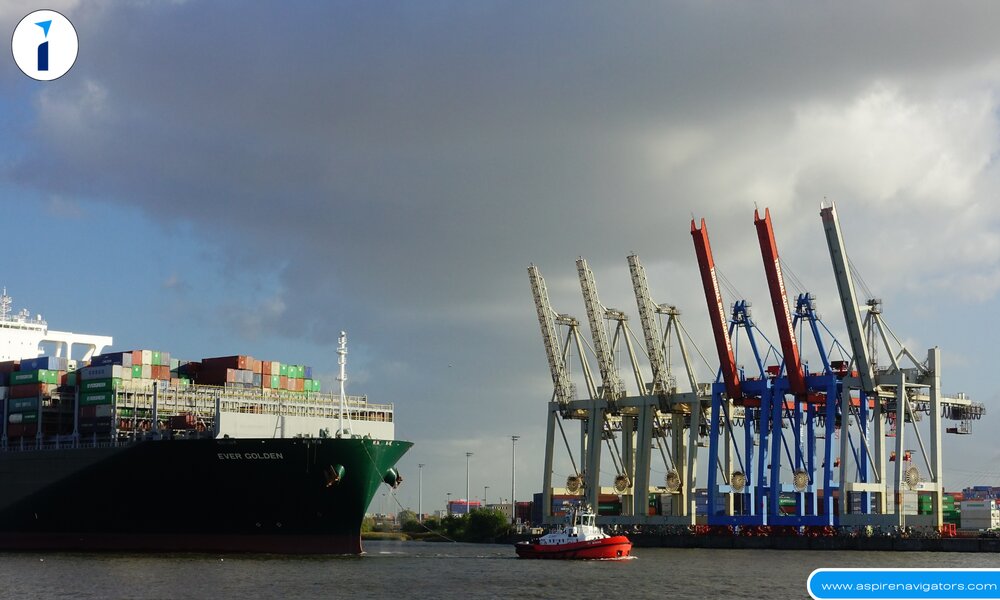
Venezuelan Oil Reserves and Its Impact on Global Markets
Venezuela boasts the largest oil reserves in the world, but its ability to produce and export oil has been significantly reduced due to ongoing political instability, mismanagement, and sanctions. This has had a profound impact on the global oil market and Venezuela’s standing in global energy politics.
Oil Production Crisis: Venezuela’s oil production has dropped to historical lows, partly due to the lack of foreign investment and skilled workforce.
Global Oil Prices: As one of the major oil-producing nations, fluctuations in Venezuela’s oil production have contributed to global price shifts.
How the U.S. Actions Affect Venezuelan Oil Funds
The U.S. has implemented various measures to prevent the misallocation of Venezuela’s oil wealth, redirecting funds from Venezuela’s government to humanitarian aid and other areas designed to mitigate the impact on the civilian population. The goal is to force the Venezuelan government to return to democratic norms without exacerbating the suffering of ordinary Venezuelans.
U.S. Actions and Venezuela’s Struggling Oil Industry
The ongoing conflict between the U.S. and Venezuela over oil assets is far from simple. While U.S. sanctions aim to destabilize Venezuela’s regime, they also cause collateral damage to the country’s ability to use its oil wealth for economic recovery. Understanding the intricate web of sanctions, oil debts, and production issues is crucial for grasping the larger geopolitical picture in this crisis.
Visit: Leaders Spotlight